Length of ECDSA Signatures
Shows distribution of ECDSA signature length per day.Length of ECDSA signatures
The ECDSA signatures used in Bitcoin consist of the encoded r and S-values and a Signature Hash.
The r and S-values make up the largest parts of the signature.
Both are 256 bit big-endian, signed integers normally taking up 32 bytes.
The highest bit of the value indicates its signed-ness in the DER encoding (0 is positive and 1 is negative).
However, ECDSA requires the values to be unsigned integers.
Thus the r and S-values are padded with an extra 0x00 byte if the highest bit indicates a negative value (highest bit is 1).
64 byte for the r and S-values, a DER encoding overhead of 6 bytes and one byte for the Signature Hash results in a signature length of 71 bytes.
If either the r or the S-value has the highest bit set then it needs extra padding of 1 byte which results in a 72-byte-signature.
If the highest bits of both values are set, then both need padding of one byte each resulting in a 73-byte-signature.
6 byte | DER encoding overhead
32 byte | r-value
(1 byte) | r-value padding (if needed)
32 byte | S-value
(1 byte) | S-value padding (if needed)
1 byte | Signature Hash
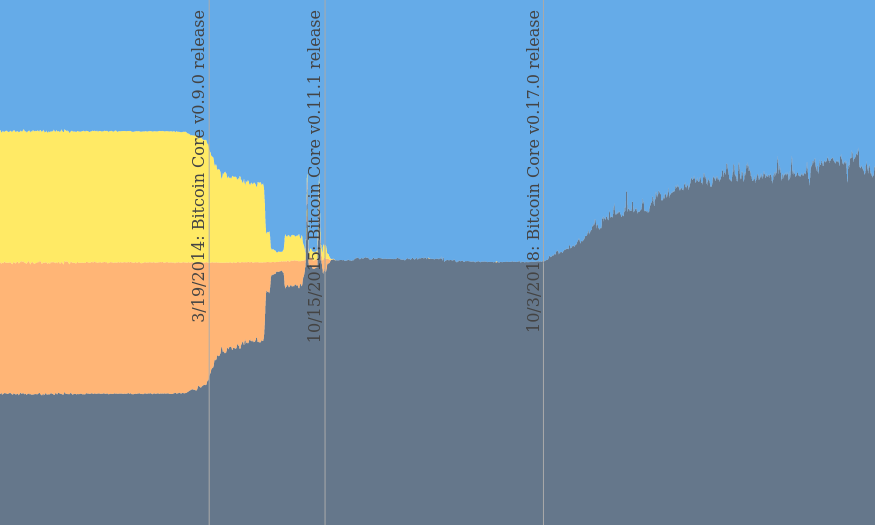
Evolution of the signature length
Between 2010 and 2014 the distribution of ECDSA signature sizes remained fairly constant.
A 25-50-25 percent split of 71-byte, 72-byte, and 73-byte-signatures can be observed.
This is the result of the r and S-values being random and thus each needing padding in half of the cases.
The 71-byte-signatures have no padding, 72-byte-signatures have padding either for the r-value or the S-value, and the 73-byte-signatures have padding both values.
The percentage of 73-byte-signatures began to shrink with the release of Bitcoin Core v0.9.0 in March of 2014.
This release included a malleability breaker in Bitcoin Core wallet.
The wallet would only generate so-called low-s signatures that don’t need padding of the S-value.
This results in 72-byte or 71-byte-signatures.
Other wallets started producing signatures with only low-s-values as transaction malleability became more and more of a problem.
With the release of Bitcoin Core v0.10.3 and Bitcoin Core v0.11.1 in October 2015 high-s signatures (the opposite of low-s signatures) were made non-standard to removed a transaction malleability vector.
Over the following three years, half of the signatures were 71-byte and the other half were 72-byte long.
Only low-s signatures were standard which requires no padding byte.
The required r-value padding, however, did add a byte in half of the signatures resulting in a length of 72-byte.
The Bitcoin Core v0.17.0 in October 2018 included an improvement to the wallet code that would only produce low-r signatures that don’t require a padding byte. This has been picked up by other wallets, such as the Electrum Bitcoin Wallet, in late 2019.
Related Charts

DER encoded ECDSA Signatures
Shows the distribution of DER-encoded ECDSA signatures per day.
S-values in ECDSA Signatures
Shows the distribution of low and high S-values in ECDSA signatures per day.
Total ECDSA Signature size
Shows total size of ECDSA signatures in Gigabyte.